Preparing for Asian Longhorned Tick in Kentucky
ENTFACT-518: Preparing for Asian Longhorned Tick in Kentucky | Download PDF
By Anna Pasternak, Graduate Tick Researcher and Jonathan L. Larson, Extension Entomologist
Asian Longhorned Tick Fast Facts
- Asian longhorned tick (ALT) is an invasive species that was first confirmed in the United States in 2013 with further discoveries in 2017.
- This tick species reproduces through parthenogenesis, where the female can produce offspring on her own. This can result in thousands of ticks being found on animals.
- As of this writing, ALT has been found in Floyd, Martin, Metcalfe, Madison, Breathitt, Perry, Boone, Garrard, Barren, and Laurel counties.
- ALT can vector Theileria to cattle and can cause extreme blood loss in wildlife and farm animals, careful monitoring of livestock and use of veterinary tick prevention methods is highly recommended.
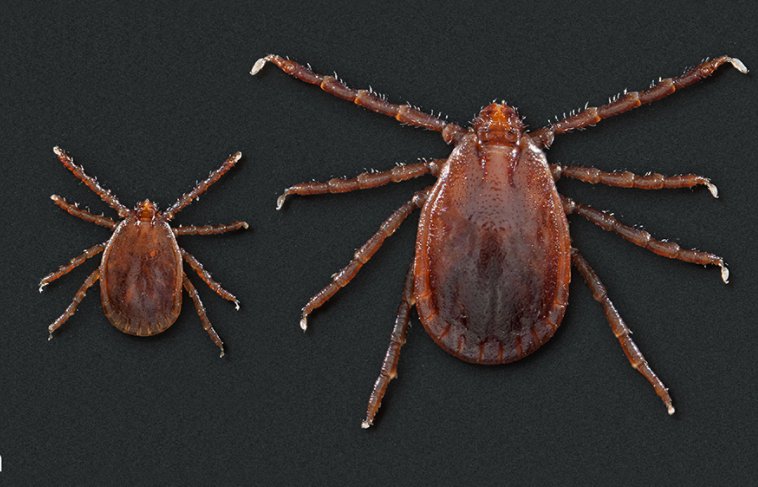

Asian longhorned tick (ALT) is an invasive species that is brown in color with little to no distinguishing markings. They are smaller than many of our native ticks. Photo by Centers for Disease Control.
Pest Background and Description
The Asian longhorned tick (ALT) is an invasive species that was first confirmed in the US in New Jersey, in 2013 with subsequent confirmations in 2017. Since these initial finds, ALT has spread to multiple other states. It is native to East Asia, including the nations of China, Japan, and Korea.
ALT is a simple looking tick. They have a reddish-brown coloration throughout their life. Like native species, they progress from eggs to larva, to nymphs, then to adults. The larval stage only has six legs while nymphs and adults both have eight. As adults, ALT are about .1 inch long (2.5 mm) and are smaller than many of our native tick species. As they feed, their bodies will swell to the proportions of a pea. Unlike native species, such as the American dog tick or Lonestar tick, the Asian longhorned tick has no distinct patterns or markings. So far, all Asian longhorned ticks caught in the United States have been female. The species reproduces here through parthenogenesis, where an adult female can give birth to many clonal female daughters.
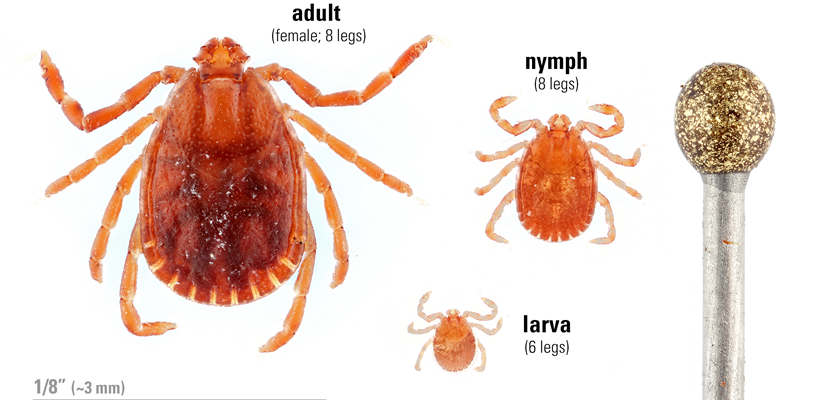
Asian longhorned tick go from egg to larva, to nymph, then to adult. They are reddish brown throughout their life and quite small (the gold object is the head of a pin). Photo by Matt Bertone, NC State Entomology.
Threat Posed By Asian Longhorned Ticks
Asian longhorned tick, like other problematic tick species, is a blood feeding ectoparasite. They will await a host by questing on vegetation (such as long grass). When a potential host wanders by, the tick will climb onto the body and then search for a suitable feeding site. Following this, they will insert their mouthparts into the host and begin to draw blood out. They will feed for multiple days until fully engorged.
So far, ALT has been confirmed on 25 different animal hosts including but not limited to; turkeys, squirrels, rabbits, raccoons, elk, deer, and bear. Domesticated animals such as cattle, sheep, and horses are also under threat. There have been confirmed bites on humans, but the CDC indicates that there is less attraction to humans than to other animals.
This tick is a possible vector for the pathogens responsible for spotted fevers and for anaplasmosis. There are ongoing research projects in the US to find if ALT is going to be a competent vector for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and Lyme disease. While the most recent research has demonstrated that ALT is unlikely to be a vector for Lyme disease, this is an ongoing situation that requires continued evaluation. There has been a published report showing that a wild caught tick contained the pathogen, but no confirmed cases of the tick transferring the pathogen to a host have been recorded. As for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, one trial demonstrated that ALT can transmit the bacteria responsible, but thus far, no wild caught Asian longhorned ticks have contained the pathogen. This situation will also require careful monitoring in the future.
Despite the lack of pathogen transfer, ALT does pose a threat to wild and domestic animals. As these ticks are capable of reproducing through parthenogenesis, an individual female tick is capable of creating hundreds of more ticks that will feed on an animal. As these populations boom on a host, the animal can suffer from anemia and ultimately exsanguination is possible. Two cases of lambs dying in Tennessee due to blood loss as a result of these ticks has been recorded.
What Is The Situation In The US Right Now?
As of the revision of this fact sheet, there have been confirmed finds of ALT in: Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Indiana, Georgia, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia.
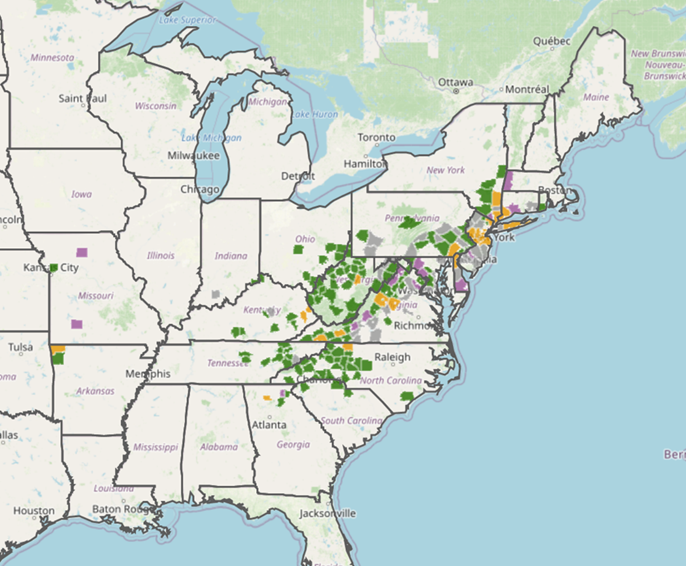
The known distribution of Asian longhorned tick in the US. This map is taken from the National Haemaphysalis longicornis (Asian longhorned tick) Situation Report as of mid-2023.
In Kentucky specifically, ALT has been found in Floyd, Martin, Metcalfe, Madison, Breathitt, Perry, Boone, Garrard, Barren, and Laurel counties. Instances of Asian longhorned tick in Kentucky tend to be associated with cattle, though there are reports from bear, elk, and humans as well.
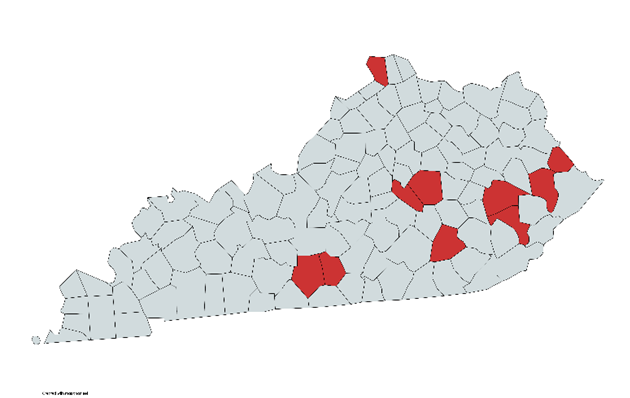
In Kentucky, Asian longhorned tick has been found in at least 10 counties, Floyd, Martin, Metcalfe, Madison, Breathitt, Perry, Boone, Garrard, Barren, and Laurel counties
Theileria
Asian longhorned tick is considered a competent vector for the cattle disease Theileria, more specifically, Theileria orientalis Ikeda. Theileria is a protozoon that can infect red and white blood cells, causing anemia in infected cattle. The symptoms include anemia, jaundice, weakness, and increased abortions. Theileria is often mistaken for anaplasmosis. Pregnant heifers and calves are susceptible to infection. Mortality rates from Theileria can vary wildly from herd to herd, but infected individuals that survive can suffer relapses and become lifelong carriers of the pathogen.
In 2022 Theileria was found in both Tennessee and Kentucky. As Asian longhorned tick furthers its range in the two states, it is possible more of them could be infected with the pathogen responsible for Theileria, escalating infections in the state’s cattle. Beef producers need to keep a close eye on their herds for Asian longhorned tick and for the symptoms of Theileria and consult with their veterinarian if they are considered their herd is infected. Cattle that live through the infection can still be sold for meat and Theileria will not infect a human.
Tick Prevention and Management
As with all ticks, people can take precautionary steps to keep themselves safe from ALT bites. Using repellants for your skin (such as DEET or picaridin) can help but treating your clothing with permethrin will provide the best protection. Permethrin is not to be used on the skin and should only be applied to clothing items. Performing routine tick checks after spending time in tick habitat will also hopefully intercept ticks before they bite.
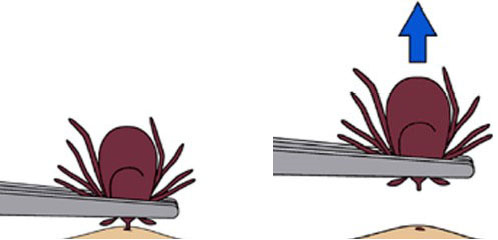
If you find that a tick (of any species) has attached itself to you, there are steps you should take to remove the tick. Avoid using methods such as fire, alcohol, essential oils, or other topical applications that will kill or agitate the tick while it is attached to you. If you use these, you might induce the tick to “vomit” into you, increasing the possibility of pathogens being transferred to you. Instead, find a pair of fine point tweezers and grip the tick’s body as close to your skin as possible. Then, pull steadily out to remove the tick. Do not rip the tick out or twist and wiggle it out, doing this could cause pieces of the tick to break off inside of you.
As for animals, treating your pets with tick preventive medicine will keep them tick-free and help to prevent them from accidentally bringing the little bloodsuckers into your yard and house. Livestock should be inspected thoroughly at regular intervals to hopefully find ticks on animals before populations are able to explode. When they are located on animals, removing them as you would on a human is the best course of action. Habitat management can help suppress tick populations as well. Be sure to cut down on long vegetation near pastures and barns and remove brush piles where possible. Keeping an approximately 9-foot wide, open perimeter near pastures can help minimize tick populations in high animal traffic areas. Perimeters can be treated with pyrethroid products (such as bifenthrin) though this should not be done to entire pastures. Products that can be wipe-on or spray repellents as well as shampoos, ear tags, pour on insecticides and dusts can help to repel some ticks for a short while. These treatments may offer protection for four to eight hours and even if they are used, careful monitoring of the animals is still required.
Revised: 7/2023
CAUTION! Pesticide recommendations in this publication are registered for use in Kentucky, USA ONLY! The use of some products may not be legal in your state or country. Please check with your local county agent or regulatory official before using any pesticide mentioned in this publication.
Of course, ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW LABEL DIRECTIONS FOR SAFE USE OF ANY PESTICIDE!
