Controlling Stored Product Pests Using Low Temperature
ENTFACT-635: Controlling Stored Product Pests Using Low Temperature | Download PDF
by Ric Bessin, Extension Specialist
University of Kentucky College of Agriculture
Several species of stored products insects can infest dried fruit, cereal and grain products in the pantry as well as birdseed, pet foods and some types of holiday decorations. Often problems are overlooked until moths or wandering larvae alert the homeowner to the presence of a serious infestation. Usually, the best solution is to examine all grain products and dispose of any infested materials. Cabinets and shelving should be vacuumed to remove flour and other food material from cracks and crevices that can provide these pests with a food source. Without thorough sanitation, new products will continue to become infested. Upon opening, new cereal and grain products should be stored in closed tightly sealed metal, plastic or glass containers.
Occasionally, it may be necessary to try to salvage infested items such as holiday decorations or homegrown popcorn that may have a few "bugs". Low temperature can be used to deinfest small quantities of dried fruit, cereal and grain products. In general, the lower the temperature, the less time that is required to kill the pests. The following table provides the number of days at specific temperature ranges necessary to kill all stages of the common stored products pests.
After the pests have been controlled, care should be taken to prevent reinfestation of these items. See ENTFACT-612, Stored Products Pests in the Pantry, for descriptions of the common stored products pests and additional control measures.
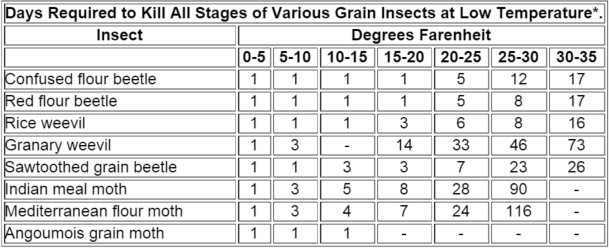
*Adapted from: Richard T. Cotton. Pests of Stored Grain and Grain Products.
Revised: 11/19
CAUTION! Pesticide recommendations in this publication are registered for use in Kentucky, USA ONLY! The use of some products may not be legal in your state or country. Please check with your local county agent or regulatory official before using any pesticide mentioned in this publication.
Of course, ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW LABEL DIRECTIONS FOR SAFE USE OF ANY PESTICIDE!
Images: University of Kentucky Entomology
