Parasitic Mites of Humans
ENTFACT-637: Parasitic Mites of Humans | Download PDF
by Michael F. Potter, Extension Entomologist
University of Kentucky College of Agriculture
Mites are very small arthropods which are closely related to ticks. Mite larvae have six legs whereas the nymphal and adult stages have eight. Most species of mites are pests of agricultural crops. However, certain types of mites are parasitic on humans.
Chiggers
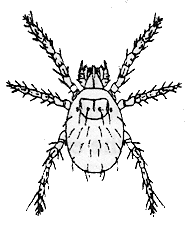
Chigger
Chiggers are the larvae of a family of mites that are sometimes called red bugs. The adults are large, red mites often seen running over pavement and lawns. Chiggers are extremely small (0.5 mm) and are difficult to see without magnification. The six-legged larvae are hairy and yellow-orange or light red. They are usually encountered outdoors in low, damp places where vegetation is rank and grass and weeds are overgrown. Some species also infest drier areas, however, making it difficult to predict where an infestation will occur.
Chiggers overwinter as adults in the soil, becoming active in the spring. Eggs are laid on the soil. After hatching, the larvae crawl about until they locate and attach to a suitable host. The larvae do not burrow into the skin, but inject a salivary fluid which produces a hardened, raised area around them. Body fluids from the host are withdrawn through a feeding tube. Larvae feed for about 4 days and then drop off and molt to nonparasitic nymphs and adults. Chiggers feed on a variety of wild and domestic animals, as well as humans. The life cycle (from egg to egg) is completed in about 50 days.
Most people react to chigger bites by developing reddish welts within 24 hours. Intense itching accompanies the welts, which may persist for a week or longer if not treated. Bites commonly occur around the ankles, waistline, armpits, or other areas where clothing fits tightly against the skin. Besides causing intense itching, chigger bites that are scratched may result in infection and sometimes fever. Chiggers in North America are not known to transmit disease.
Persons walking in chigger-infested areas can be protected by treating clothing (cuffs, socks, waistline, sleeves) or exposed skin with tick repellents. Some repellents should only be used on clothing; and it is important to follow label directions. People who suspect they may have been attacked by chiggers should take a soapy bath immediately and apply antiseptic to any welts. A local anesthetic will provide temporary relief from itching.
Regular mowing and removal of weeds and brush make areas less suitable for chiggers and their wild hosts. Mowing also enhances penetration and performance of miticides, should they be required. Chigger populations can be further reduced by treating infested areas with residual miticides. Applications should be thorough but restricted to areas frequented and suspected of being infested.
Human Scabies
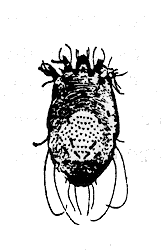
Scabies Mite
The sarcoptic itch mites, Sarcoptes scabei, infest the skin of a variety of animals including humans. The types of Sarcoptes inhabiting the skin of mammals are all considered forms of Sarcoptes scabei and can exchange hosts to some degree. (For example, Canine scabies can be temporarily transferred from dogs to humans, causing itching and lesions on the waist, chest and forearms.)
Human scabies mites are very small and are rarely seen. They commonly attack the thin skin between the fingers, the bend of the elbow and knee, the penis, breasts, and the shoulder blades. The mites burrow into the skin, making tunnels up to 3 mm (0.1 inch) long. When they first burrow into the skin, the mites cause little irritation, but after about a month, sensitization begins. A rash appears in the area of the burrows and intense itching is experienced.
Scabies mites are transmitted by close personal contact, usually from sleeping in the same bed. Bedridden individuals in institutions (e.g., nursing homes) may also pass the mites from caregiver to patient. The adult fertilized female mite is usually the infective life stage. She adheres to the skin using suckers on her legs and burrows into the skin where she lays her oval eggs. In 3 to 5 days these eggs hatch into larvae and move freely over the skin. Soon they transform into nymphs and reach maturity 10 to 14 days after hatching.
A scabies infestation should be handled as a medical problem and is readily diagnosed and treated by most physicians. (Confirmation requires isolating the mites in a skin scraping.) The first step to control a scabies infestation usually involves softening the skin with soap and water to make sure the pesticide treatments can penetrate well. An evening bath followed by overnight treatment works best. A total body (neck- down) application of topical pesticide medication should remain for 8-12 hours before showering in the morning. Commonly used products include lindane (Kwell (tm)), permethrin (Elimite (tm)) and crotamiton (Eurax (tm)). Follow directions on the product package carefully.
Because the symptoms of scabies mite infestations are delayed by about a month, other members of the household besides those showing symptoms may be harboring the mites. It is important that everyone in the infected family or living group go through the treatment regime. A second treatment may be necessary to eliminate an infestation of scabies mites, but patients should avoid overzealous pesticide treatment since itching may persist for a week or more after treatment and does not necessarily indicate treatment failure.
Scabies mites cannot live off of a human host for more than 24 hours. Therefore, insecticide treatment of premises is not warranted. It is recommended, however, that coincident with treatment, the clothing and bedding from infested individuals be washed in hot water or dry cleaned.
Bird and Rodent Mites
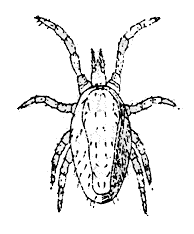
Bird Mite
Parasitic mites that occasionally infest buildings are usually associated with wild or domestic birds or rodents. Bird and rodent mites normally live on the host or in their nests, but migrate to other areas of the structure when the animal dies or abandons the nest. Rodent mites often become a nuisance after an infestation of mice or rats has been eliminated. People usually become aware of the problem when they are attacked by mites searching for an alternate food source. Their bites cause moderate to intense itching and irritation. Rodent and bird mites are very tiny, but usually can be seen with the naked eye. They are about the size of the period at the end of this sentence.
The first step in controlling bird or rodent mites is to eliminate the host animals and remove their nesting sites. Often, the nests will be found in the attic, around the eaves and rafters, or in the gutters or chimney. Gloves should be used when handling dead animals. A respirator should also be worn when removing nest materials to avoid inhaling fungal spores and other potential disease-producing organisms associated with the droppings.
After nests are removed, the areas adjacent to the nest should be sprayed or dusted with a residual insecticide such as those products labeled for flea control. Space or ULV treatments with non-residual materials (e.g., synergized pyrethrins) can be used in conjunction with residual sprays. Space treatments are especially useful when the mite infestation has dispersed widely from the nesting site. In this case, more extensive treatment with residual and non-residual insecticides may also be necessary in other areas of the structure where mites are observed. A vacuum cleaner or cloth moistened with alcohol can be used to eliminate mites crawling on open surfaces.
Revised: 10/96
CAUTION! Pesticide recommendations in this publication are registered for use in Kentucky, USA ONLY! The use of some products may not be legal in your state or country. Please check with your local county agent or regulatory official before using any pesticide mentioned in this publication.
Of course, ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW LABEL DIRECTIONS FOR SAFE USE OF ANY PESTICIDE!
Photos: M. Potter, University of Kentucky Entomology
